行为型 - 迭代器(Iterator)
Iterator 模式也正是用来解决对一个聚合对象的遍历问题,将对聚合的遍历封装到一个类中进行,这样就避免了暴露这个聚合对象的内部表示的可能。
[[toc]]
概念
Iterator 模式典型的结构图为:
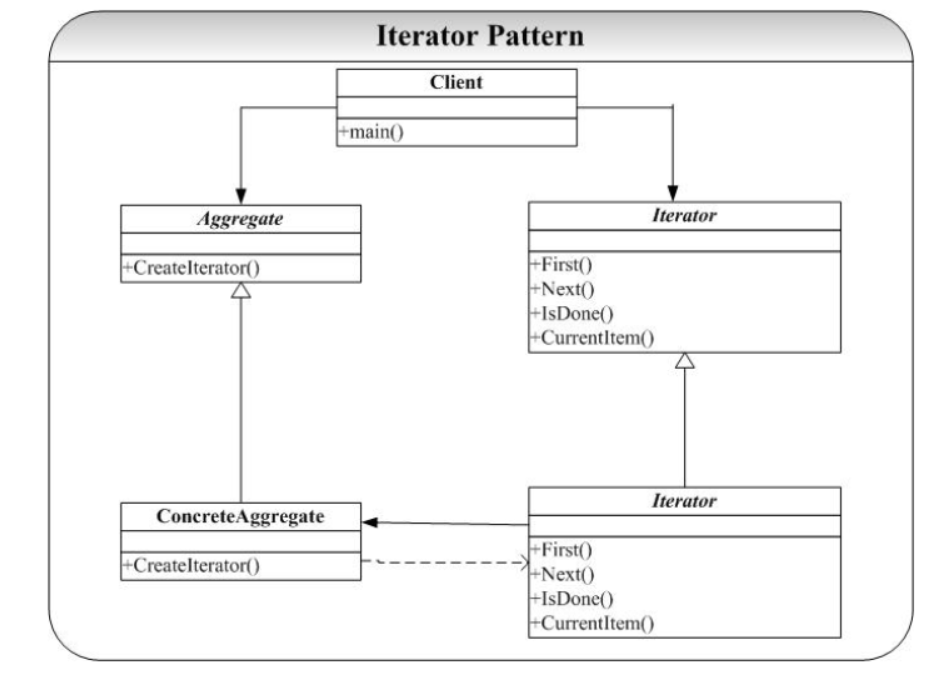
Iterator 模式中定义的对外接口可以视客户成员的便捷定义,但是基本的接口在图中的Iterator 中已经给出了(参考 STL 的 Iterator 就知道了)。———— 迭代器可以用于对统一类型的处理,Java 使用Iterable<T>来作入参类型,可以忽略到底是数组还是链表。
代码实现
#ifndef _AGGREGATE_H_
#define _AGGREGATE_H_
class Iterator;
typedef int Object;
class Interator;
class Aggregate
{
public:
virtual ~Aggregate();
virtual Iterator *CreateIterator() = 0;
virtual Object GetItem(int idx) = 0;
virtual int GetSize() = 0;
protected:
Aggregate();
private:
};
class ConcreteAggregate : public Aggregate
{
public:
enum
{
SIZE = 3
};
ConcreteAggregate();
~ConcreteAggregate();
Iterator *CreateIterator();
Object GetItem(int idx);
int GetSize();
protected:
private:
Object _objs[SIZE];
};
#endif //~_AGGREGATE_H_
#include "Aggregate.h"
#include "Iterator.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Aggregate::Aggregate()
{
}
Aggregate::~Aggregate()
{
}
ConcreteAggregate::ConcreteAggregate()
{
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
_objs[i] = i;
}
ConcreteAggregate::~ConcreteAggregate()
{
}
Iterator *ConcreteAggregate::CreateIterator()
{
return new ConcreteIterator(this);
}
Object ConcreteAggregate::GetItem(int idx)
{
if (idx < this->GetSize())
return _objs[idx];
else
return -1;
}
int ConcreteAggregate::GetSize()
{
return SIZE;
}
#ifndef _ITERATOR_H_
#define _ITERATOR_H_
class Aggregate;
typedef int Object;
class Iterator
{
public:
virtual ~Iterator();
virtual void First() = 0;
virtual void Next() = 0;
virtual bool IsDone() = 0;
virtual Object CurrentItem() = 0;
protected:
Iterator();
private:
};
class ConcreteIterator : public Iterator
{
public:
ConcreteIterator(Aggregate *ag, int idx = 0);
~ConcreteIterator();
void First();
void Next();
bool IsDone();
Object CurrentItem();
protected:
private:
Aggregate *_ag;
int _idx;
};
#endif //~_ITERATOR_H_
#include "Iterator.h"
#include "Aggregate.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Iterator::Iterator()
{
}
Iterator::~Iterator()
{
}
ConcreteIterator::ConcreteIterator(Aggregate *ag, int idx)
{
this->_ag = ag;
this->_idx = idx;
}
ConcreteIterator::~ConcreteIterator()
{
}
Object ConcreteIterator::CurrentItem()
{
return _ag->GetItem(_idx);
}
void ConcreteIterator::First()
{
_idx = 0;
}
void ConcreteIterator::Next()
{
if (_idx < _ag->GetSize())
_idx++;
}
bool ConcreteIterator::IsDone()
{
return (_idx == _ag->GetSize());
}
#include "Iterator.h"
#include "Aggregate.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Aggregate *ag = new ConcreteAggregate();
Iterator *it = new ConcreteIterator(ag);
for (; !(it->IsDone()); it->Next())
{
cout << it->CurrentItem() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Iterator 模式的实现代码很简单,实际上为了更好地保护 Aggregate 的状态,我们可以尽量减小 Aggregate 的 public 接口,而通过将 Iterator 对象声明位 Aggregate 的友元来给予 Iterator一些特权,获得访问 Aggregate 私有数据和方法的机会。
应用
Iterator 模式的应用很常见,在开发中就经常会用到 STL 中预定义好的 Iterator 来对 STL 类进行遍历( Vector、 Set 等)。
