第4章:序列式容器 heap
heap概述
heap并不归属于STL容器组件,扮演priority queue的助手,binary max heap适合作为priority queue的底层机制,priority queue允许用户以任意次序将元素推入容器,但是取出是一定是优先权最高(数值最高)的元素先出来。binary heap是一种complete binary tree(完全二叉树),整棵binary tree除了最底层的叶子节点外是填满的,而最底层的叶子节点由左至右不得有空隙,如下图所示:
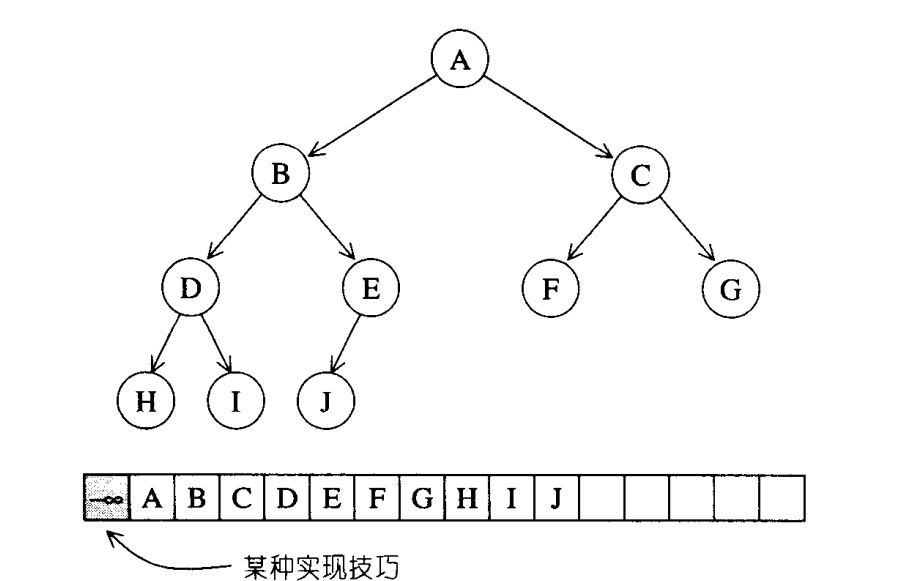
利用array来存储completebinary tree的所有节点,将array的#0元素保留,**那么当complete binary tree的某个节点位于array的i处时,其左子节点必位于array的2i处,右子节点必位于array的2i+1处,父节点必位于i/2处。**根据元素排列方式,heap分为max-heap和min-heap两种,前者每个节点的键值都大于或等于其子节点的值,后者每个节点的键值都小于或等于其子节点的值。max-heap中最大值在根节点,min-heap最小值在根节点。底层存储结构为vector或者array。STL 供应的是max-heap。heap的所有元素都必须遵循特别的排列规则,所以heap不提供遍历功能,也不提供迭代器。
heap算法
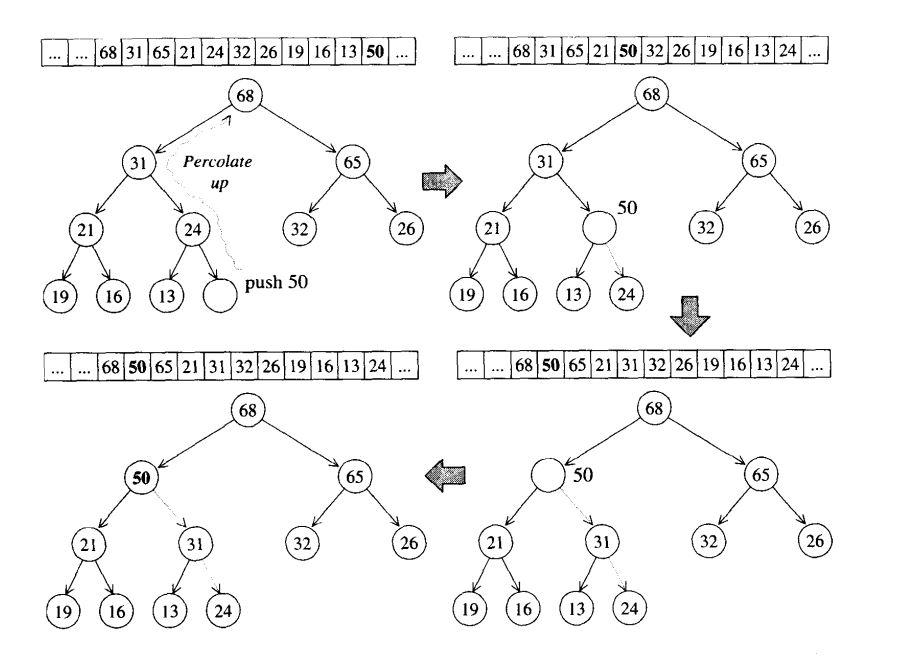
## push_heap算法
push_heap算法:将新加入的元素放在最下层的叶节点,即vector的end()处,还需满足max-heap条件,执行所谓的percolate up(上溯)过程,即不断比较新节点和其父节点,最终将其放到合适的位置。举例如下:
代码实现:
template<class RandomAccessIterator>
inline void push_heap(RandomAccessIterator first,RandomAccessIterator last){
//这个函数被调用时,新元素已经放在底部容器的最尾端
_push_heap_aux(first,last,distance_type(first),value_type(first));
}
template<class RandomAccessIterator,class Distance,class T>
inline void _push_heap_aux(RandomAccessIterator first,RandomAccessIterator last,Distance*,T*)
{_push_heap(first ,Distance((last-first)-1),Distance(0),T(*(last-1)));}
template<class RandomAccessIterator,class Distance,class T>
void _push_heap(RandomAccessIterator first,Distance holeIndex,Distance topIndex,T value)
{
Distence parent=(holeIndex-1)/2;//找出父节点
while(holeIndex>topIndex&&*(first+parent)<value){
//未到达顶端,父节点小于新值,使用<,所以STL heap是个max_heap。
*(first+holeIndex)=*(first +parent)//父值下移
holeIndex=parent;//调整位置,向上提升至父节点
parent=(holeIndex-1)/2;//找到新的父节点。
}//持续到顶端,或者满足heap的特性就停止了。
*(first+holeIndex)=value;//找到它应该处于的位置,插入操作结束。
}
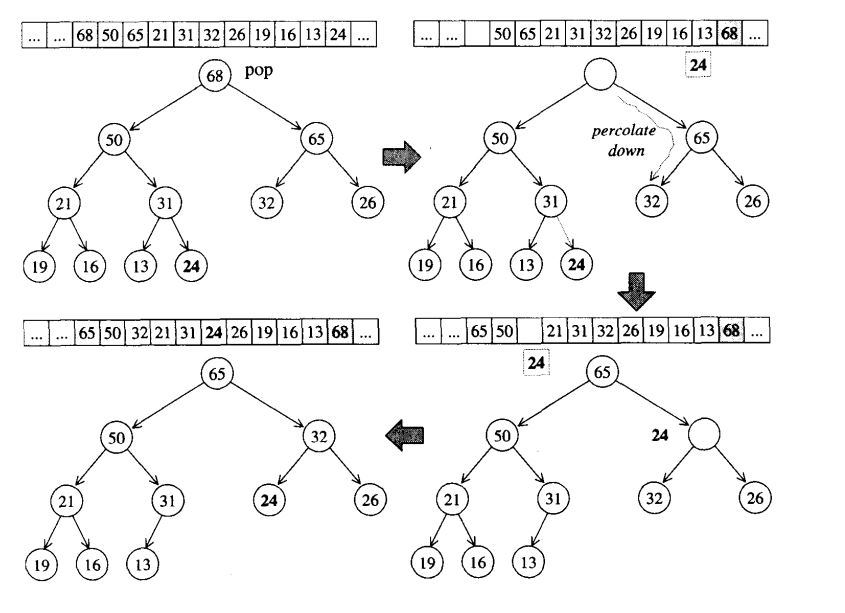
pop_heap
pop_heap算法:pop操作直接取根节点,为了满足max-heap条件,必须割舍最下层最右边的叶节点,并将其值重新安插至max-heap。为了满足max-heap次序特性,先执行percolate down(下溯)过程:将空间节点和其较大子节点“对调”,并持续下放,直至叶节点;然后将前述被割舍的元素值赋值给这个“已到达叶层的空洞节点”,再对它执行一次percolate up(上溯)过程,即可完成结构调整。
template <class RandomAccessIterator>//提供首尾两个迭代器,否则结果不可预知。
inline void pop_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last) {
__pop_heap_aux(first, last, value_type(first));
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class T>
inline void __pop_heap_aux(RandomAccessIterator first,
RandomAccessIterator last, T*) {
__pop_heap(first, last - 1, last - 1, T(*(last - 1)), distance_type(first));
// pop动作的結果为底层容器的第一個元素。因此,首先设定欲调整值为尾值,然后將首值調至
// 尾节点(所以以上將迭代器result设为last-1)。然后重整 [first, last-1),
// 使之重新成一個合格的 heap。
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class T, class Distance>
inline void __pop_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
RandomAccessIterator result, T value, Distance*) {
*result = *first; // 設定尾值为首值,于是尾值即是結果,
// 可由调用底层容器之 pop_back() 取出尾值。
__adjust_heap(first, Distance(0), Distance(last - first), value);
// 以上欲重新調整 heap,洞号为 0,欲調整值为value。
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class Distance, class T>
void __adjust_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, Distance holeIndex,
Distance len, T value) {
Distance topIndex = holeIndex;
Distance secondChild = 2 * holeIndex + 2; // 洞节点之右子节点
while (secondChild < len) {
// 比较洞节点之左右兩个子值,然后以 secondChild 代表较大子节点。
if (*(first + secondChild) < *(first + (secondChild - 1)))
secondChild--;
// Percolate down:令较大大子值为洞值,再令洞号下移至较大子节点处。
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + secondChild);
holeIndex = secondChild;
// 找出新洞节点的右子节点
secondChild = 2 * (secondChild + 1);
}
if (secondChild == len) { // 沒有右子节点,只有左子节点
// Percolate down:令左子值为洞值,再令洞号下移至左子节点处。
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + (secondChild - 1));
holeIndex = secondChild - 1;
}
// 將欲调整值填入目前的洞号內。注意,此時肯定滿足次序特性。
// 依侯捷之见,下面直接改為 *(first + holeIndex) = value; 应该可以。
__push_heap(first, holeIndex, topIndex, value);
}
//此时的最大元素只是被放置在了底部容器的尾端,并未被取走,所以要取值,可以使用底部容器提供的back()操作函数,如果要移除,使用pop_back().
注意:pop_heap后,最大元素只是被置于底层容器的最尾部,尚未被取走。如果取值,可用back函数;如果移除,可用pop_back函数。
## sort_heap
既然每一pop_heap都将最大值放到vector的末尾,那么如果每次都缩小pop_heap的参数范围(从后向前缩减一个与元素),那么最终得到的vector将是一个递增序列。
// 以下這個 sort_heap() 不允許指定「大小比較標準」
template <class RandomAccessIterator>
void sort_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last) {
// 以下,每執行一次 pop_heap(),極值(在STL heap中為極大值)即被放在尾端。
// 扣除尾端再執行一次 pop_heap(),次極值又被放在新尾端。一直下去,最後即得
// 排序結果。
while (last - first > 1)
pop_heap(first, last--); // 每執行 pop_heap() 一次,操作範圍即退縮一格。
}
## make_heap
make_heap,将一段现有的数据转化成一个heap,代码如下:
// 將 [first,last) 排列為一個 heap。
template <class RandomAccessIterator>
inline void make_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last) {
__make_heap(first, last, value_type(first), distance_type(first));
}
// 以下這組 make_heap() 不允許指定「大小比較標準」。
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class T, class Distance>
void __make_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, T*,
Distance*) {
if (last - first < 2) return; // 如果長度為 0 或 1,不必重新排列。
Distance len = last - first;
// 找出第一個需要重排的子樹頭部,以 parent 標示出。由於任何葉節點都不需執行
// perlocate down,所以有以下計算。parent 命名不佳,名為 holeIndex 更好。
Distance parent = (len - 2) / 2;//找出第一个有子节点的节点
while (true) {
// 重排以 parent 為首的子樹。len 是為了讓 __adjust_heap() 判斷操作範圍
__adjust_heap(first, parent, len, T(*(first + parent)));//下溯程序
if (parent == 0) return; // 排序到根節點,程序就結束。
parent--; // (重排之子樹的)頭部向前一個節點,迭代过程,排序完一个就接着排序前一个。
}
}
heap测试实例
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
{
// test heap (以vector完成)
int ia[9] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 9, 3, 5};
vector<int> ivec(ia, ia + 9);
make_heap(ivec.begin(), ivec.end());
for (int i = 0; i < ivec.size(); ++i) {
cout << ivec[i] << " "; // 9 5 8 3 4 0 2 3 1
}
cout << endl;
ivec.push_back(7);
push_heap(ivec.begin(), ivec.end());
for (int i = 0; i < ivec.size(); ++i) {
cout << ivec[i] << " "; // 9 5 8 3 4 0 2 3 1 4
}
cout << endl;
pop_heap(ivec.begin(), ivec.end());
cout << ivec.back() << endl; // 9
ivec.pop_back();
for (int i = 0; i < ivec.size(); ++i) {
cout << ivec[i] << " "; // 8 7 4 3 5 0 2 3 1
}
cout << endl;
sort_heap(ivec.begin(), ivec.end());
for (int i = 0; i < ivec.size(); ++i) {
cout << ivec[i] << " "; // 0 1 2 3 3 4 5 7 8
}
cout << endl;
}
{
// test heap (以array完成)
int ia[9] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 9, 3, 5};
make_heap(ia, ia+9);
// array无法动态改变大小,因此不可以对满载的 array做 push_heap()动作。
//因为那得先在 array尾端增加㆒个元素。
sort_heap(ia, ia+9);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i) {
cout << ia[i] << " "; // 0 1 2 3 3 4 5 8 9
}
cout << endl;
make_heap(ia, ia+9);
pop_heap(ia, ia+9);
cout << ia[8] << endl; // 9
}
{
// test heap (底层以 array完成)
int ia[6] = {4,1,7,6,2,5};
make_heap(ia, ia+6);
for(int i=0; i<6; ++i)
cout << ia[i] << ' '; // 7 6 5 1 2 4
cout << endl;
}
}
