第4章:序列式容器 slist
slist概述
SGI STL另提供一个单向链表slist。slist和list的主要差别在于,前者的迭代器属于单向的Forward Iterator,后者的迭代器属于双向的BidirectionalIterator。根据STL的习惯,插入操作会将新元素插入于指定位置之前。**作为单向链表,slist没有任何方便的方法可以回头定出前一个位置,因此它必须从头找起。**为此,slist特别提供了insert_after和erase_after函数供灵活调用。
insert函数的实现如下,__slist_previous函数可以根据头节点_M_head和位置节点__pos找到__pos之前的那个节点,然后调用_M_insert_after函数,实际调用__slist_make_link,在__pos-1节点后创建以__x为值的节点:
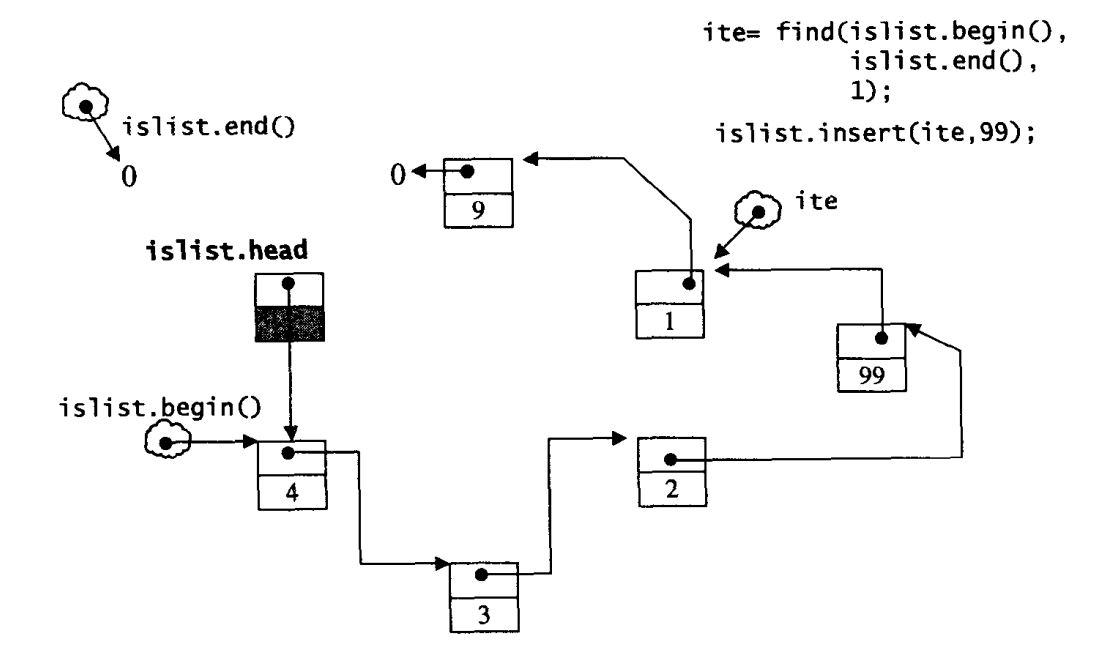
islist.insert(ite, 99);
iterator insert(iterator __pos, const value_type& __x) {
return iterator(_M_insert_after(__slist_previous(&this->_M_head,
__pos._M_node),
__x));
}
inline _Slist_node_base* __slist_previous(_Slist_node_base* __head,
const _Slist_node_base* __node)
{
while (__head && __head->_M_next != __node)
__head = __head->_M_next;
return __head;
}
_Node* _M_insert_after(_Node_base* __pos, const value_type& __x) {
return (_Node*) (__slist_make_link(__pos, _M_create_node(__x)));
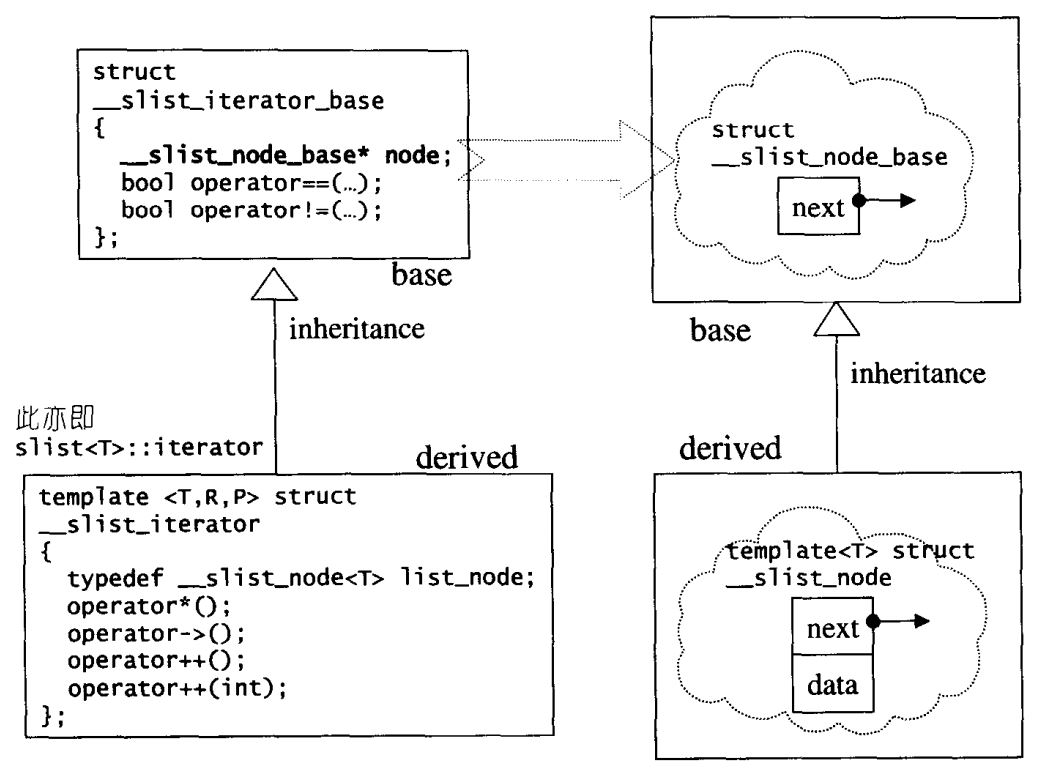
slist的节点
slist的节点和迭代器设计架构如下:
slist的迭代器
slist的迭代器可以用下图表示:
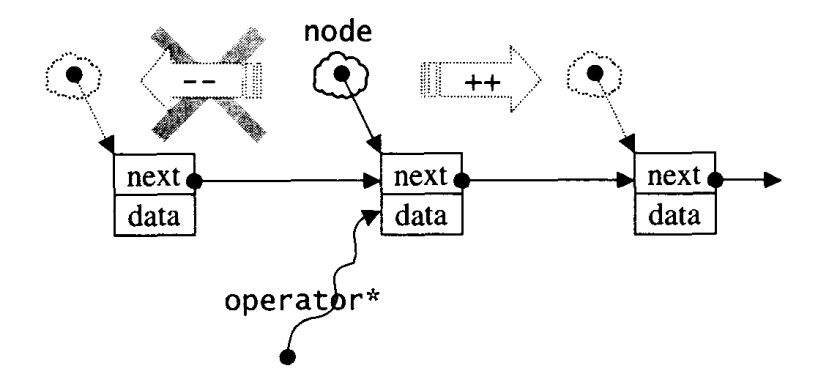
slist的数据结构
template<class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class slist
{
public :
typedef T value_type ;
typedef value_type* pointer ;
typedef const value_type* const_pointer ;
typedef value_type& reference ;
typedef const value_type& const_reference ;
typedef size_t size_type ;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type ;
typedef __slist_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator ;
typedef __slist_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator ;
private :
typedef __slist_node<T> list_node ;
typedef __slist_node_base list_node_base ;
typedef __slist_iterator_base iterator_base ;
typedef simple_alloc<list_node,Alloc> list_node_allocator ;
static list_node* create_node(const value_type& x)
{
list_node* node = list_node_allocator:;allocate() ; //配置空间
__STL_TRY{
construct(&node->data,x) ;
node->next = 0 ;
}
__STL_UNWIND(list_node_allocator:;deallocate(node)) ;
return node ;
}
static void destroy_node(list_node* node)
{
destroy(&node->data) ; //将元素析构
list_node_allocator::deallocate(node) ; //释放空间
}
private :
list_node_base head ; //头部。注意,它不是指针,是实物
public:
slist() {head.next = 0 ;}
~slist(){clear() ;}
public :
iterator begin() {return iterator((list_node*)head.next) ;}
iterator end() {return iteator(0) ;}
iterator size() {const __slist_size(head.next) ;}
bool empty() const {return head.next == 0 ;}
//两个slist互换:只要将head交换互指即可
void swap(slist &L)
{
list_node_base* tmp = head.next;
head.next = L.head.next ;
L.head.next = tmp ;
}
public :
//取头部元素
reference front() {return ((list_node*)head.next)->data ;}
//从头部插入元素(新元素成为slist的第一个元素)
void push_front(const value_type& x)
{
__slist_make_link(&head,create_node(x)) ;
}
//注意,没有push_back()
//从头部取走元素(删除之)。修改head
void pop_front()
{
list_node* node = (list_node*)head.next ;
head.next = node->next ;
destroy_node(node);
}
.....
} ;
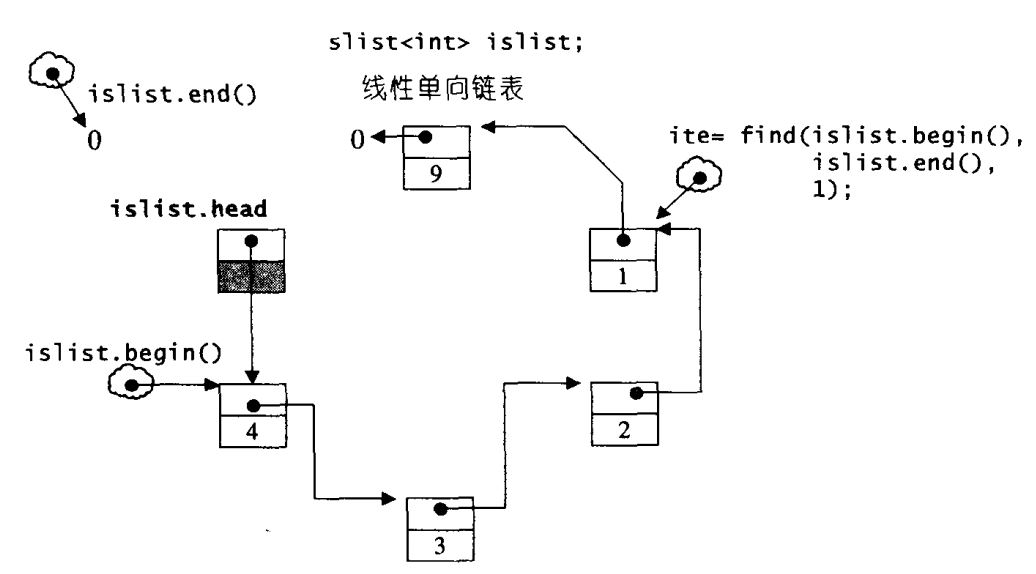
slist的测试实例
// file: 4slist-test.cpp
// mingw64没有这个库
//#include <slist>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int i;
slist<int> islist;
cout << "size=" << islist.size() << endl;
islist.push_front(9);
islist.push_front(1);
islist.push_front(2);
islist.push_front(3);
islist.push_front(4);
cout << "size=" << islist.size() << endl;
slist<int>::iterator ite =islist.begin();
slist<int>::iterator ite2=islist.end();
for(; ite != ite2; ++ite)
cout << *ite << ' '; // 4 3 2 1 9
cout << endl;
ite = find(islist.begin(), islist.end(), 1); //使用STL的find函数,可以找到1之前的那个迭代器
if (ite!=0)
islist.insert(ite, 99);
cout << "size=" << islist.size() << endl; // size=6
cout << *ite << endl; // 1
ite =islist.begin();
ite2=islist.end();
for(; ite != ite2; ++ite)
cout << *ite << ' '; // 4 3 2 99 1 9
cout << endl;
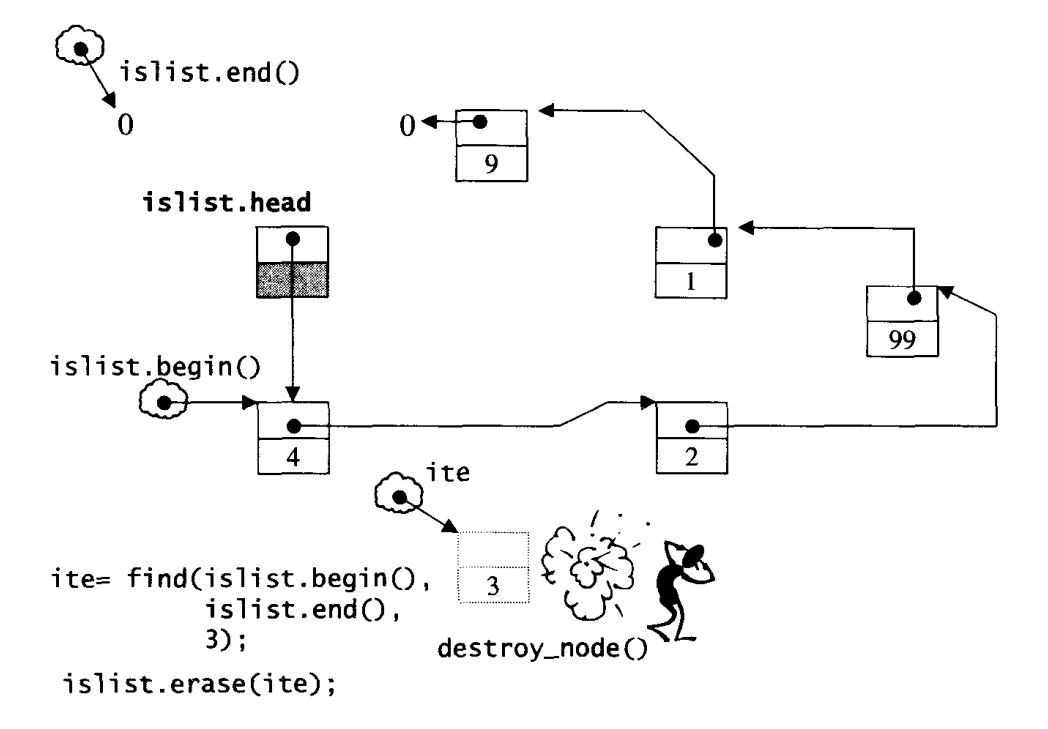
ite = find(islist.begin(), islist.end(), 3);
if (ite!=0)
cout << *(islist.erase(ite)) << endl; // 2
ite =islist.begin();
ite2=islist.end();
for(; ite != ite2; ++ite)
cout << *ite << ' '; // 4 2 99 1 9
cout << endl;
}
上述执行过程的示意图如下: