第5章:关联式容器 RB-tree
RB-tree概述
首先介绍一下基本概念,二叉树:任何节点最多只有两个子节点,这两个子节点分别称为左子节点和右子节点。二叉搜索树:任何节点的键值一定大于其左子树中的每一个节点的键值,小于其右子树中的每一个节点的键值。所谓的RB-tree不仅是二叉搜索树,而且必须满足以下规则:
- 每个节点不是红色就是黑色。
- 根节点为黑色。
- 如果节点为红色,其子节点必须为黑色。
- 任意一个节点到到NULL(树尾端)的任何路径,所含之黑色节点数必须相同。
根据规则4,新增节点必须为红色;根据规则3,新增节点之父节点必须为黑色。当新增节点根据二叉搜索树的规则到达其插入点时,却未能符合上述条件时,就必须调整颜色并旋转树形,如下图:
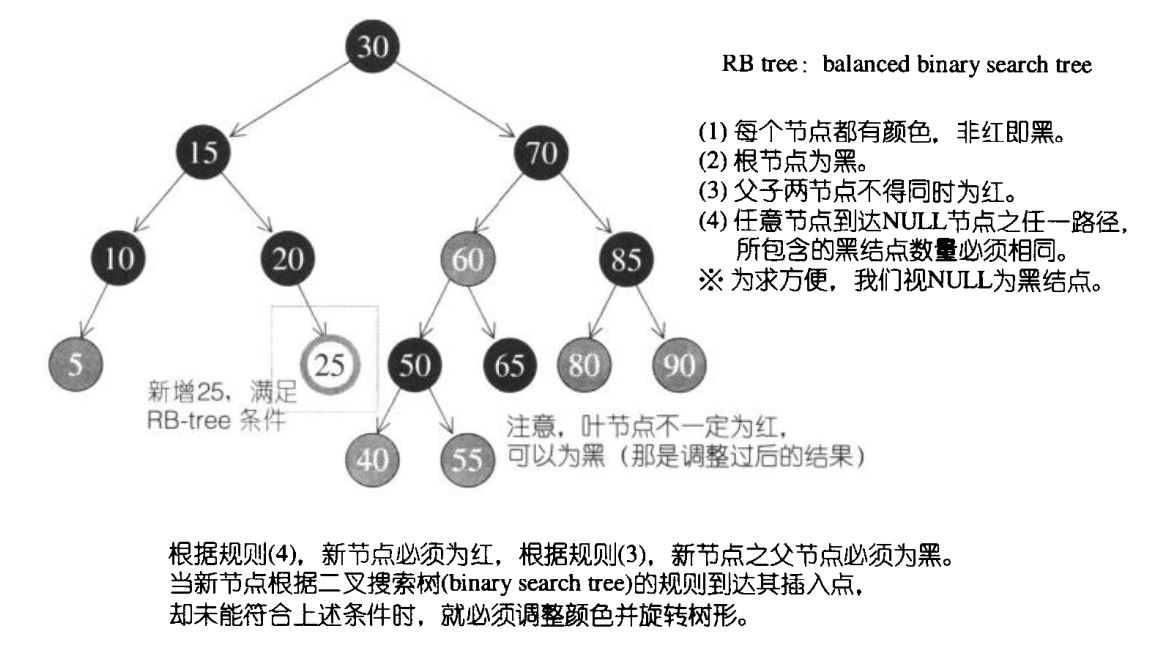
插入节点,会导致不满足RB-tree的规则条件,经历左旋和右旋等操作,使得重新满足规则。
RB-tree节点设计
RB-tree的节点和迭代器都是双层结构,RB-tree迭代器的前进和后退操作,都是调用基础迭代器的increment和decrement实现的。如下:
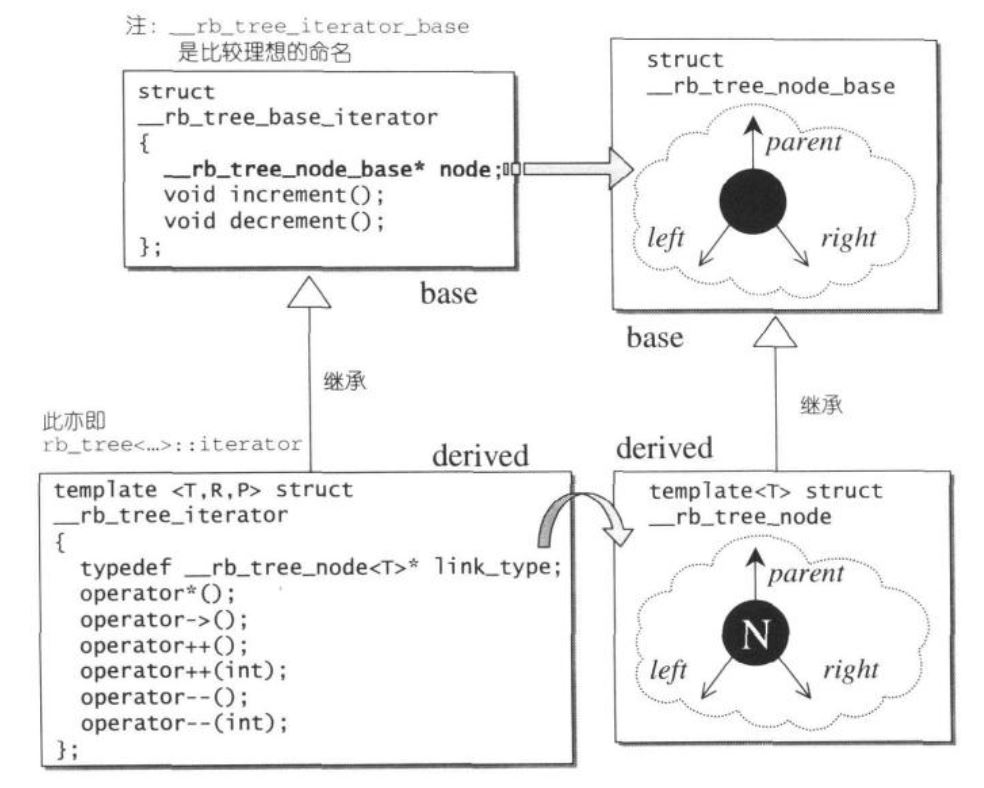
RB-tree的极值通过minimum和maximum可以方便地查找到,
typedef bool __rb_tree_color_type;
const __rb_tree_color_type __rb_tree_red = false; // 红色为0
const __rb_tree_color_type __rb_tree_black = true; // 黑色为1
struct __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type;
typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;
color_type color; // 节点颜色,红色或黑色
base_ptr parent; // 该指针指向其父节点
base_ptr left; // 指向左节点
base_ptr right; // 指向右节点
static base_ptr minimum(base_ptr x)
{
while (x->left != 0) x = x->left; //一直向左走,找到最小值
return x;
}
static base_ptr maximum(base_ptr x)
{
while (x->right != 0) x = x->right; //一直向右走,找到最大值
return x;
}
};
template <class Value>
struct __rb_tree_node : public __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type;
Value value_field; //节点值
};
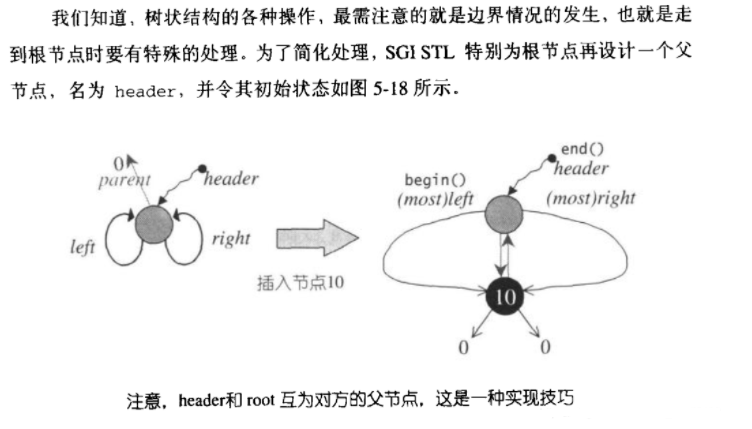
RB-tree数据结构
//stl_tree.h
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_TREE_H
#define __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_TREE_H
/*
Red-black tree(红黑树)class,用来当做SLT关联容器的底层机制(如set,multiset,map,
multimap)。里面所用的insertion和deletion方法以Cormen, Leiserson 和 Riveset所著的
《算法导论》一书为基础,但是有以下两点不同:
(1)header不仅指向root,也指向红黑树的最左节点,以便用常数时间实现begin(),并且也指向红黑树的最右边节点,以便
set相关泛型算法(如set_union等等)可以有线性时间实现。
(2)当一个即将被删除的节点有两个孩子节点时,它的successor(后继)node is relinked into its place, ranther than copied,
如此一来唯一失效的(invalidated)的迭代器就只是那些referring to the deleted node.
*/
#include <stl_algobase.h>
#include <stl_alloc.h>
#include <stl_construct.h>
#include <stl_function.h>
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare,
class Alloc = alloc>
class rb_tree {
protected:
typedef void* void_pointer;
typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;
typedef simple_alloc<rb_tree_node, Alloc> rb_tree_node_allocator;
typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type;
public:
//这里没有定义iterator,在后面定义
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Value value_type;
typedef value_type* pointer;
typedef const value_type* const_pointer;
typedef value_type& reference;
typedef const value_type& const_reference;
typedef rb_tree_node* link_type;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
protected:
link_type get_node() { return rb_tree_node_allocator::allocate(); }
void put_node(link_type p) { rb_tree_node_allocator::deallocate(p); }
link_type create_node(const value_type& x) {
link_type tmp = get_node(); // 配置空间
__STL_TRY{
construct(&tmp->value_field, x); // 构建内容
}
__STL_UNWIND(put_node(tmp));
return tmp;
}
link_type clone_node(link_type x) { // 复制一个节点(值和颜色)
link_type tmp = create_node(x->value_field);
tmp->color = x->color;
tmp->left = 0;
tmp->right = 0;
return tmp;
}
void destroy_node(link_type p) {
destroy(&p->value_field); // 析构内容
put_node(p); // 释放内存
}
protected:
// RB-tree 只以三个资料表现
size_type node_count; // 追踪记录树的大小(节点总数)
link_type header; //这个是实现上的一个技巧
Compare key_compare; // 节点的键值比较判断准则。是个函数 function object。
//以下三个函数用来方便取得header的成员
link_type& root() const { return (link_type&)header->parent; }
link_type& leftmost() const { return (link_type&)header->left; }
link_type& rightmost() const { return (link_type&)header->right; }
//以下六个函数用来方便取得节点x的成员。x为函数参数
static link_type& left(link_type x) { return (link_type&)(x->left); }
static link_type& right(link_type x) { return (link_type&)(x->right); }
static link_type& parent(link_type x) { return (link_type&)(x->parent); }
static reference value(link_type x) { return x->value_field; }
static const Key& key(link_type x) { return KeyOfValue()(value(x)); }
static color_type& color(link_type x) { return (color_type&)(x->color); }
//和上面六个作用相同,注意x参数类型不同。一个是基类指针,一个是派生类指针
static link_type& left(base_ptr x) { return (link_type&)(x->left); }
static link_type& right(base_ptr x) { return (link_type&)(x->right); }
static link_type& parent(base_ptr x) { return (link_type&)(x->parent); }
static reference value(base_ptr x) { return ((link_type)x)->value_field; }
static const Key& key(base_ptr x) { return KeyOfValue()(value(link_type(x))); }
static color_type& color(base_ptr x) { return (color_type&)(link_type(x)->color); }
//找最大值和最小值。node class 有这个功能函数
static link_type minimum(link_type x) {
return (link_type)__rb_tree_node_base::minimum(x);
}
static link_type maximum(link_type x) {
return (link_type)__rb_tree_node_base::maximum(x);
}
public:
typedef __rb_tree_iterator<value_type, reference, pointer> iterator;
typedef __rb_tree_iterator<value_type, const_reference, const_pointer>
const_iterator;
#ifdef __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION
typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
#else /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
typedef reverse_bidirectional_iterator<iterator, value_type, reference,
difference_type>
reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_bidirectional_iterator<const_iterator, value_type,
const_reference, difference_type>
const_reverse_iterator;
#endif /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
private:
iterator __insert(base_ptr x, base_ptr y, const value_type& v);
link_type __copy(link_type x, link_type p);
void __erase(link_type x);
void init() {
header = get_node(); // 产生一个节点空间,令header指向它
color(header) = __rb_tree_red; // 令 header 尾红色,用來区 header
// 和 root(在 iterator.operator++ 中)
root() = 0;
leftmost() = header; // 令 header 的左孩子为自己。
rightmost() = header; // 令 header 的右孩子为自己。
}
public:
//默认构造函数 // allocation/deallocation
rb_tree(const Compare& comp = Compare())
: node_count(0), key_compare(comp) {
init();
}
// 以另一个 rb_tree x 初始化
rb_tree(const rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>& x)
: node_count(0), key_compare(x.key_compare)
{
header = get_node();
color(header) = __rb_tree_red;
if (x.root() == 0) { // 如果 x 空树
root() = 0;
leftmost() = header;
rightmost() = header;
}
else { // x 不是空树
__STL_TRY{
root() = __copy(x.root(), header); // 拷贝红黑树x
}
__STL_UNWIND(put_node(header));
leftmost() = minimum(root()); // 令 header 的左孩子为最小节点
rightmost() = maximum(root()); // 令 header 的右孩子为最大节点
}
node_count = x.node_count;
}
~rb_tree() {
clear();
put_node(header);
}
rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>&
operator=(const rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>& x);
public:
// accessors:
Compare key_comp() const { return key_compare; }
iterator begin() { return leftmost(); } // RB 树的起始为最左(最小节点)
const_iterator begin() const { return leftmost(); }
iterator end() { return header; } // RB 树的终节点为header所指处
const_iterator end() const { return header; }
reverse_iterator rbegin() { return reverse_iterator(end()); }
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const {
return const_reverse_iterator(end());
}
reverse_iterator rend() { return reverse_iterator(begin()); }
const_reverse_iterator rend() const {
return const_reverse_iterator(begin());
}
bool empty() const { return node_count == 0; }
size_type size() const { return node_count; }
size_type max_size() const { return size_type(-1); }
void swap(rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>& t) {
//RB-tree只有三个资料表现成员,所以两颗RB-tree互换时,只需互换3个成员
__STD::swap(header, t.header);
__STD::swap(node_count, t.node_count);
__STD::swap(key_compare, t.key_compare);
}
public:
// insert/erase
// 将 x 安插到 RB-tree 中(保持节点值独一无二)。
pair<iterator, bool> insert_unique(const value_type& x);
// 将 x 安插到 RB-tree 中(允许重复节点)
iterator insert_equal(const value_type& x);
iterator insert_unique(iterator position, const value_type& x);
iterator insert_equal(iterator position, const value_type& x);
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class InputIterator>
void insert_unique(InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
template <class InputIterator>
void insert_equal(InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
void insert_unique(const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
void insert_unique(const value_type* first, const value_type* last);
void insert_equal(const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
void insert_equal(const value_type* first, const value_type* last);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
void erase(iterator position);
size_type erase(const key_type& x);
void erase(iterator first, iterator last);
void erase(const key_type* first, const key_type* last);
void clear() {
if (node_count != 0) {
__erase(root());
leftmost() = header;
root() = 0;
rightmost() = header;
node_count = 0;
}
}
public:
// 集合(set)的各种操作行为
iterator find(const key_type& x);
const_iterator find(const key_type& x) const;
size_type count(const key_type& x) const;
iterator lower_bound(const key_type& x);
const_iterator lower_bound(const key_type& x) const;
iterator upper_bound(const key_type& x);
const_iterator upper_bound(const key_type& x) const;
pair<iterator, iterator> equal_range(const key_type& x);
pair<const_iterator, const_iterator> equal_range(const key_type& x) const;
public:
// Debugging.
bool __rb_verify() const;
};
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
inline bool operator==(const rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>& x,
const rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>& y) {
return x.size() == y.size() && equal(x.begin(), x.end(), y.begin());
}
//重载<运算符,使用的是STL泛型算法<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">lexicographical_compare</span>
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
inline bool operator<(const rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>& x,
const rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>& y) {
return lexicographical_compare(x.begin(), x.end(), y.begin(), y.end());
}
#ifdef __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
inline void swap(rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>& x,
rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>& y) {
x.swap(y);
}
#endif /* __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER */
//重载赋值运算符=
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>&
rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::
operator=(const rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>& x) {
if (this != &x) {//防止自身赋值
// Note that Key may be a constant type.
clear();//先清除
node_count = 0;
key_compare = x.key_compare;
if (x.root() == 0) {
root() = 0;
leftmost() = header;
rightmost() = header;
}
else {
root() = __copy(x.root(), header);
leftmost() = minimum(root());
rightmost() = maximum(root());
node_count = x.node_count;
}
}
return *this;
}
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
typename rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::iterator
rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::
__insert(base_ptr x_, base_ptr y_, const Value& v) {
//参数x_为新值安插点,参数y_为安插点之父节点,参数v 为新值
link_type x = (link_type)x_;
link_type y = (link_type)y_;
link_type z;
//key_compare是键值得比较准则,是个函数或函数指针
if (y == header || x != 0 || key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(y))) {
z = create_node(v); // 产生一个新节点
left(y) = z; // 这使得当y为header时,leftmost()=z
if (y == header) {
root() = z;
rightmost() = z;
}
else if (y == leftmost()) // 如果y为最左节点
leftmost() = z; // 维护leftmost(),使它永远指向最左节点
}
else {
z = create_node(v);
right(y) = z; // 令新节点成为安插点之父节点y的右孩子
if (y == rightmost())
rightmost() = z; // 维护rightmost(),使它永远指向最右节点
}
parent(z) = y; // 设定新节点的父节点
left(z) = 0; // 设定新孩子节点的左孩子
right(z) = 0; // 设定新孩子节点的右孩子
// 新节点的颜色将在 __rb_tree_rebalance() 设定并调整
__rb_tree_rebalance(z, header->parent); // 参数一为新增节点,参数二为root
++node_count; // 节点数增加
return iterator(z); // 返回迭代器,指向新增节点
}
// 安插新值;允许键值重复。返回新插入节点的迭代器
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
typename rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::iterator
rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::insert_equal(const Value& v)
{
link_type y = header;
link_type x = root();
while (x != 0) { // 从根节点开始,向下寻找适当安插位置
y = x;
x = key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(x)) ? left(x) : right(x);
}
return __insert(x, y, v);
}
/*
不允许键值重复,否则安插无效。
返回值是个pair,第一个元素是个RB-tree迭代器,指向新增节点。
第二个元素表示安插是否成功。
*/
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
pair<typename rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::iterator, bool>
rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::insert_unique(const Value& v)
{
link_type y = header;
link_type x = root(); //从根节点开始
bool comp = true;
while (x != 0) { // 从根节点开始向下寻找适当安插位置
y = x;
comp = key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(x)); // v 键值小于目前节点的键值?
x = comp ? left(x) : right(x); // 遇「大」往左,遇「小于或等于」往右
}
//离开while循环之后,y所指即为安插点的父节点,x必为叶子节点
iterator j = iterator(y); // 令迭代器j指向安插点之父节点 y
if (comp) //如果离开while循环时comp为真,表示 父节点键值>v ,将安插在左孩子处
if (j == begin()) // 如果j是最左节点
return pair<iterator, bool>(__insert(x, y, v), true);
// 以上,x 为安插点,y 为安插点之父节点,v 为新值。
else // 否则(安插点之父节点不是最左节点)
--j; // 调整 j,回头准备测试...
if (key_compare(key(j.node), KeyOfValue()(v)))
// 小于新值(表示遇「小」,将安插于右侧)
return pair<iterator, bool>(__insert(x, y, v), true);
//若运行到这里,表示键值有重复,不应该插入
return pair<iterator, bool>(j, false);
}
template <class Key, class Val, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
typename rb_tree<Key, Val, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::iterator
rb_tree<Key, Val, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::insert_unique(iterator position,
const Val& v) {
if (position.node == header->left) // begin()
if (size() > 0 && key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(position.node)))
return __insert(position.node, position.node, v);
// first argument just needs to be non-null
else
return insert_unique(v).first;
else if (position.node == header) // end()
if (key_compare(key(rightmost()), KeyOfValue()(v)))
return __insert(0, rightmost(), v);
else
return insert_unique(v).first;
else {
iterator before = position;
--before;
if (key_compare(key(before.node), KeyOfValue()(v))
&& key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(position.node)))
if (right(before.node) == 0)
return __insert(0, before.node, v);
else
return __insert(position.node, position.node, v);
// first argument just needs to be non-null
else
return insert_unique(v).first;
}
}
template <class Key, class Val, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
typename rb_tree<Key, Val, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::iterator
rb_tree<Key, Val, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::insert_equal(iterator position,
const Val& v) {
if (position.node == header->left) // begin()
if (size() > 0 && key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(position.node)))
return __insert(position.node, position.node, v);
// first argument just needs to be non-null
else
return insert_equal(v);
else if (position.node == header) // end()
if (!key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(rightmost())))
return __insert(0, rightmost(), v);
else
return insert_equal(v);
else {
iterator before = position;
--before;
if (!key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(before.node))
&& !key_compare(key(position.node), KeyOfValue()(v)))
if (right(before.node) == 0)
return __insert(0, before.node, v);
else
return __insert(position.node, position.node, v);
// first argument just needs to be non-null
else
return insert_equal(v);
}
}
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class K, class V, class KoV, class Cmp, class Al> template<class II>
void rb_tree<K, V, KoV, Cmp, Al>::insert_equal(II first, II last) {
for (; first != last; ++first)
insert_equal(*first);
}
template <class K, class V, class KoV, class Cmp, class Al> template<class II>
void rb_tree<K, V, KoV, Cmp, Al>::insert_unique(II first, II last) {
for (; first != last; ++first)
insert_unique(*first);
}
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
template <class K, class V, class KoV, class Cmp, class Al>
void
rb_tree<K, V, KoV, Cmp, Al>::insert_equal(const V* first, const V* last) {
for (; first != last; ++first)
insert_equal(*first);
}
template <class K, class V, class KoV, class Cmp, class Al>
void
rb_tree<K, V, KoV, Cmp, Al>::insert_equal(const_iterator first,
const_iterator last) {
for (; first != last; ++first)
insert_equal(*first);
}
template <class K, class V, class KoV, class Cmp, class A>
void
rb_tree<K, V, KoV, Cmp, A>::insert_unique(const V* first, const V* last) {
for (; first != last; ++first)
insert_unique(*first);
}
template <class K, class V, class KoV, class Cmp, class A>
void
rb_tree<K, V, KoV, Cmp, A>::insert_unique(const_iterator first,
const_iterator last) {
for (; first != last; ++first)
insert_unique(*first);
}
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
RB-tree的构造与内存管理
RB-tree的元素操作
RB-tree提供两种插入操作**:insert_unique()和insert_equal()**,前者标识被插入节点的键值(key)在整棵树中必须独一无二(因此,如果整棵树中已存在相同的键值,插入操作就不会真正进行),后者标识被插入节点的键值在整棵树中可以重复,因此,无论如何插入都会成功(除非空间不足导致配置失败)。
